At a Glance

How It Works
Relenza (zanamivir) is an inhaled antiviral medicine that blocks a protein (neuraminidase) on the flu virus so it cannot spread easily in the body.- It works only against influenza A and B viruses, not against colds or other infections.
- It is most effective when started within 48 hours of flu symptoms or soon after exposure to someone with flu.
- By limiting virus spread, it can shorten illness and reduce the chance of getting the flu after close contact.
Treatment and Efficacy
Approved indications: Relenza is approved to treat acute, uncomplicated influenza A and B in patients 7 years and older who have had symptoms for no more than 2 days, and to prevent influenza A and B in patients 5 years and older, such as after close contact with someone with flu or during community outbreaks.
Off‑label uses: Off‑label, clinicians may rarely use zanamivir for certain higher‑risk or institutional influenza situations when inhalation is feasible, but evidence is more limited than for approved uses and other antivirals (such as oral oseltamivir) are usually preferred.
Efficacy expectations: When started early, Relenza typically shortens flu illness by about 1 day and can reduce the chance of complications like ear infections and needing antibiotics in some patients; for prevention, it significantly lowers the risk of developing flu while it is taken.
Comparison to similar drugs: Compared with oral neuraminidase inhibitors, Relenza has similar antiviral effectiveness but is inhaled rather than swallowed, which can be an advantage for avoiding systemic side effects but a limitation for patients who cannot use inhalation devices or who have underlying breathing problems.
Dosage and Administration
Typical dosing for treatment: For adults and children 7 years and older, the usual dose is 10 mg (two 5‑mg inhalations) twice daily for 5 days, ideally starting within 48 hours of symptom onset.
Typical dosing for prevention: For adults and children 5 years and older after close contact with someone with flu, a common regimen is 10 mg once daily for 10 days; during community outbreaks, prevention courses may be continued for up to about 28 days as directed by a clinician.
How to take it: Relenza is taken only by oral inhalation using the supplied Diskhaler; the blister is loaded, pierced, and the powder inhaled through the mouth, not swallowed or used with any other inhaler or nebulizer. It can be taken with or without food, but doses should be spaced about 12 hours apart for treatment and about 24 hours apart for prevention.
Special instructions: People with asthma or COPD who are prescribed Relenza should use a short‑acting bronchodilator before each dose if recommended and stop Relenza and seek help if breathing worsens. Patients should complete the full prescribed course even if they start to feel better.
Missed dose: If a dose is missed, take it as soon as remembered unless it is almost time for the next dose; if it is close to the next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose and resume the regular schedule without doubling doses.
Overdose: Accidental extra inhalations are unlikely to cause serious problems in most people, but very high doses or significant breathing problems after extra doses require prompt medical evaluation and supportive care as needed.
Safety and Side Effects
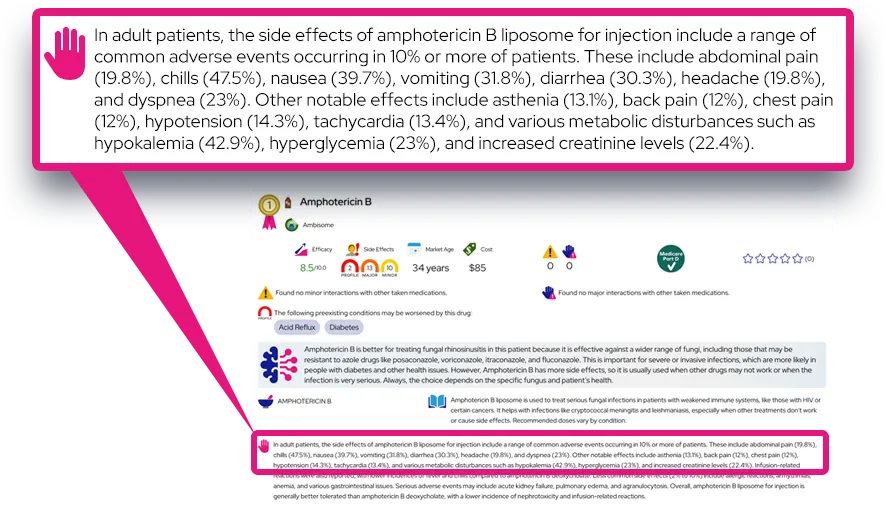
Common side effects: Common effects include cough, throat or mouth irritation, headache, and sometimes nausea; these are usually mild to moderate, begin soon after starting treatment, and often improve as the course continues.
Serious or rare adverse effects: Rare but serious problems include bronchospasm or breathing difficulty (especially in people with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), allergic reactions such as rash, swelling, or anaphylaxis, and very rarely neuropsychiatric symptoms (confusion, unusual behavior); any trouble breathing, facial or throat swelling, or severe rash needs immediate medical attention.
Warnings and precautions: Relenza is not recommended for patients with underlying airway disease like asthma or COPD unless the potential benefit clearly outweighs the risk, and if used they should have a fast‑acting bronchodilator available; it should not be used in people with severe milk protein allergy because the powder contains lactose.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, age: In pregnancy and breastfeeding, zanamivir may be considered when the expected benefit outweighs potential but not fully known risks; safety data are more limited than for some oral antivirals, so clinicians individualize decisions. It is approved for treatment from age 7 and for prevention from age 5, and is not established in younger children.
Comparative safety: Compared with some systemic antivirals, Relenza has relatively low systemic exposure and few drug–drug interactions, but carries a higher concern for breathing problems in patients with reactive airway disease.
Side‑effect reporting and safety updates: Patients and caregivers can report suspected side effects to the FDA’s MedWatch program or to the manufacturer, and updated safety information is provided through FDA safety communications and the product’s prescribing information.
Interactions and Precautions
Drug and product interactions: Because Relenza acts mainly in the airways with minimal absorption into the bloodstream, it has few known interactions with other prescription or over‑the‑counter medicines, supplements, or foods, and it does not have specific alcohol or food restrictions.
Other respiratory products: It should not be mixed in nebulizers or mechanical ventilator circuits and should only be used with its Diskhaler; people using inhaled bronchodilators or corticosteroids should generally take their usual inhaler first, then Relenza, as directed by their clinician.
Precautions and contraindications: Use is not recommended in patients with a history of severe milk protein allergy or in those who cannot use the inhaler correctly. Extra caution is needed in asthma, COPD, or other chronic lung diseases because of the risk of bronchospasm, and patients should be monitored for breathing changes.
Monitoring needs: Routine blood tests or ECG monitoring are not usually required; instead, clinical monitoring focuses on symptom improvement, breathing status, and any signs of allergic or neuropsychiatric reactions, especially in children and adolescents.
Common Questions and Answers
Q: Does Relenza cure the flu or just shorten it?
A: Relenza does not eliminate the influenza virus instantly, but when started early it can shorten how long symptoms last and may reduce the risk of some complications.
Q: Can I use Relenza if I have asthma or COPD?
A: Relenza can cause bronchospasm and is generally not recommended for people with asthma or COPD unless the expected benefit clearly outweighs the risk and a fast‑acting bronchodilator and close monitoring are in place.
Q: Is Relenza safe during pregnancy?
A: Data in pregnancy are limited, so clinicians weigh the potential benefits of treating or preventing flu against possible but not fully known risks, and may choose other antivirals depending on the specific situation.
Q: What should I do if I start Relenza more than 2 days after symptoms begin?
A: Relenza works best when started within 48 hours of flu symptoms, and starting later may give less benefit, so decisions about late use should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Q: Can Relenza be used instead of the flu vaccine?
A: No, Relenza is not a substitute for annual influenza vaccination; it is used to treat or prevent flu around the time of exposure, while vaccination helps prevent flu throughout the season.
Better Treatment, Lower Cost – No Catch.
Find safer, more effective medications with fewer side effects – often for less money. It’s fast, free, and personalized. Learn More →
Disposal Guidance
Storage: Store Relenza at room temperature, in a dry place away from moisture and heat, with the blister packs kept in their foil until use, and keep it out of reach of children and pets.
Handling: Keep the Diskhaler device clean and dry, and use only the blisters included with Relenza in that device.
Disposal: When the blister pack is empty or the medicine is no longer needed, dispose of the device and remaining blisters in household trash or through a pharmacy take‑back program if available; do not puncture or burn the device or blisters.