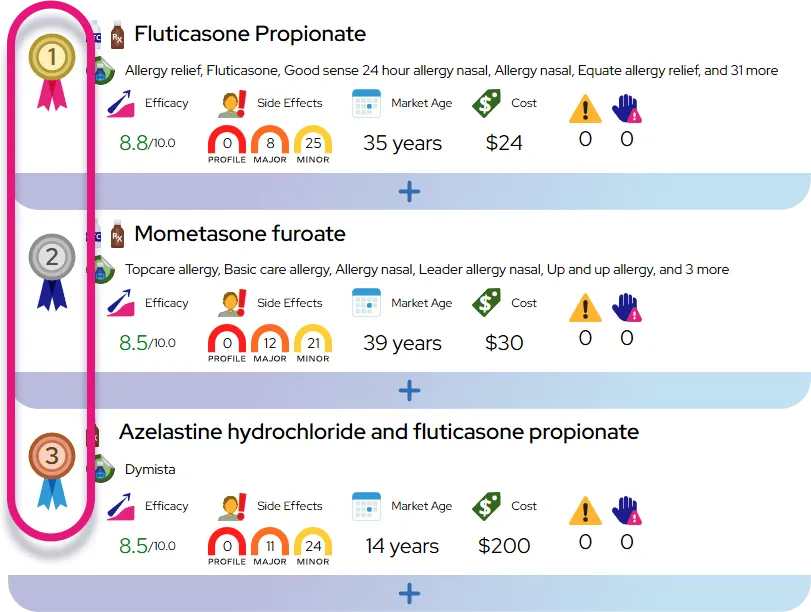
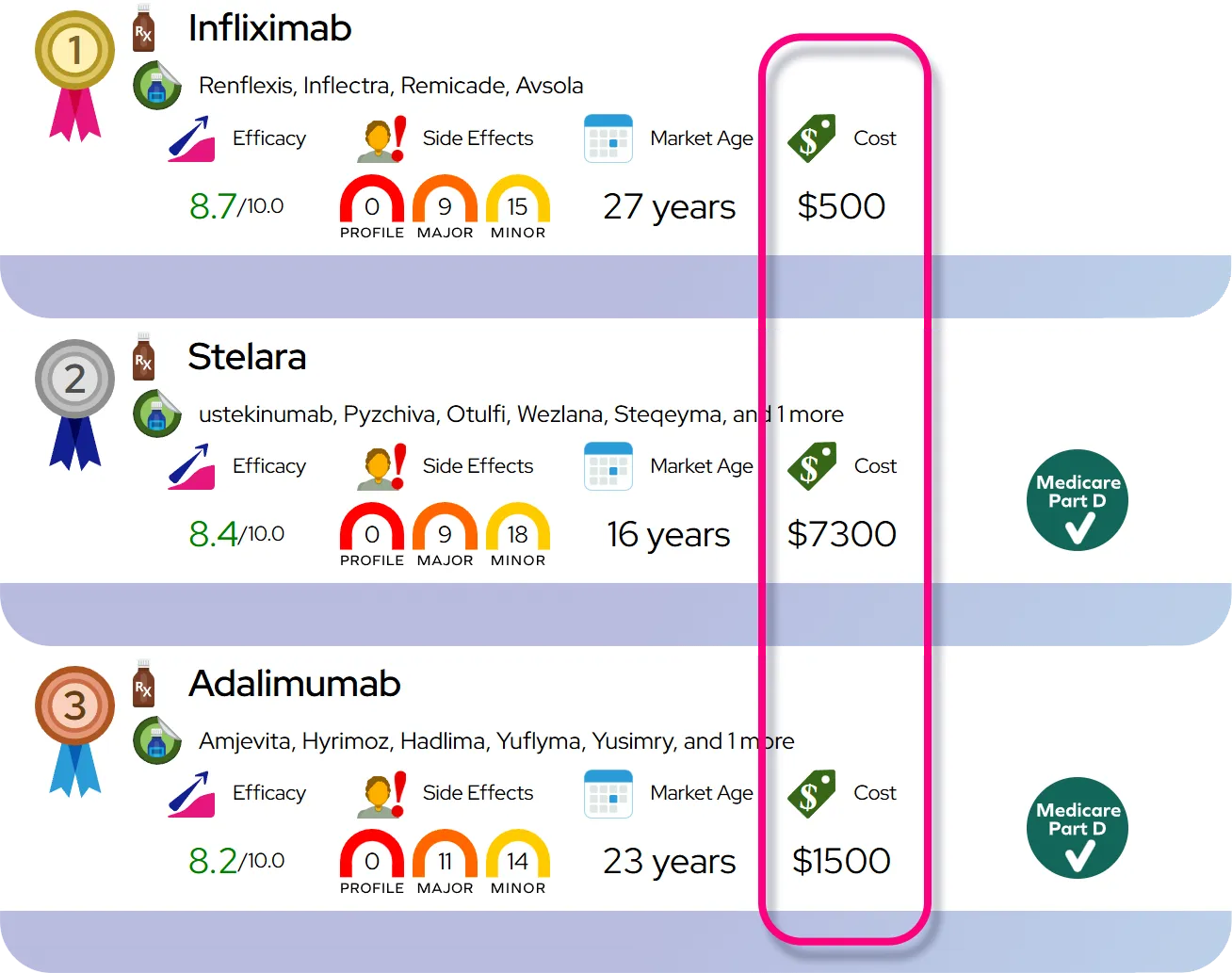
At a Glance

How It Works
This medicine is a central nervous system stimulant that increases certain natural chemicals in the brain to improve attention and control impulsive behavior.- It increases levels of norepinephrine and dopamine, which help regulate focus, alertness, and activity level.
- By strengthening signaling in parts of the brain involved in attention and self-control, it can reduce hyperactivity and impulsivity.
- Its effects begin within hours of a dose and wear off gradually over the day, depending on whether it is an immediate-release or extended-release form.
Treatment and Efficacy
Approved indications: This mixed amphetamine salts product is FDA-approved for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children, adolescents, and adults, and for narcolepsy in patients 6 years and older.
Off-label uses: Clinicians may occasionally use similar stimulant formulations off-label for conditions such as treatment-resistant depression, fatigue in certain medical illnesses, or cognitive symptoms in traumatic brain injury, but the evidence for these uses is more limited and such prescribing is usually reserved for specialists after other options have been tried.
Efficacy expectations:
- For ADHD, many people notice improved focus, less restlessness, and better task completion within the first few days at an effective dose, with full benefit often seen after dose adjustments over several weeks.
- For narcolepsy, it can reduce excessive daytime sleepiness and help patients stay awake during usual activities, though some symptoms (like cataplexy) may need additional treatments.
- Compared with other stimulant ADHD medications (such as other amphetamine or methylphenidate products), its overall effectiveness is similar; choice often depends on individual response, duration of effect needed, side-effect profile, and formulation preference (immediate- vs extended-release).
Dosage and Administration
Typical dosing and how to take: For ADHD or narcolepsy, treatment usually starts with a low dose (for example, 5 mg once or twice daily of immediate-release tablets, or a low-strength extended-release capsule once each morning) and is increased gradually based on response and tolerability; many patients fall in a total daily range of about 5–40 mg, though some adults may require higher doses under close supervision. Tablets are swallowed whole with water and can be taken with or without food, while extended-release capsules are taken once in the morning and should not be crushed or chewed (some products allow sprinkling the capsule contents on soft food, which must be swallowed without chewing).
Timing and special instructions: Doses are typically taken early in the day to reduce insomnia, and late-afternoon or evening doses are usually avoided. Take the medicine consistently as prescribed, and do not change the dose or schedule on your own. Because it is a controlled substance, refills may require a new prescription and regular follow-up visits.
Missed dose guidance: If a dose is missed, take it when remembered unless it is late in the day, in which case it is usually better to skip it and resume at the next scheduled dose to avoid sleep problems; do not double the next dose.
Overdose: Signs of overdose can include restlessness, rapid breathing, tremor, confusion, hallucinations, panic, severe nausea or vomiting, very fast or irregular heartbeat, high fever, seizures, or loss of consciousness. In case of suspected overdose, call emergency services or poison control immediately and do not wait for symptoms to worsen.
Safety and Side Effects
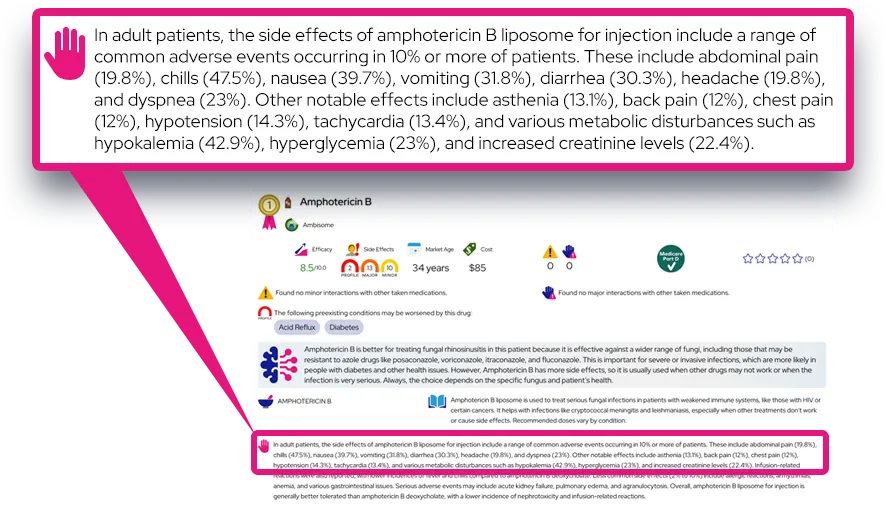
Common side effects: Frequently reported effects include decreased appetite, weight loss, trouble sleeping, dry mouth, stomach upset, nausea, headache, nervousness or anxiety, and increased heart rate or blood pressure. These are often mild to moderate, may appear in the first days to weeks of treatment, and sometimes lessen after dose adjustments or with taking the dose earlier in the day.
Serious or rare adverse effects: Seek immediate medical attention for chest pain, fainting, shortness of breath, unexplained fainting or palpitations, signs of stroke, new or worsening aggressive behavior, hallucinations, mania, severe anxiety, uncontrolled movements (tics), signs of circulation problems in fingers or toes (pain, color changes, sores), seizures, or symptoms of serotonin syndrome such as agitation, fever, rapid heartbeat, muscle stiffness, or confusion.
Warnings and precautions: This medicine should generally not be used in people with known serious structural heart disease, certain rhythm problems, or moderate-to-severe high blood pressure; it may stunt growth slightly in some children, so height and weight should be monitored. Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding requires weighing potential benefits and risks, as amphetamines can cross the placenta and enter breast milk and may affect the baby. Caution and possible dose adjustments are needed in severe kidney disease, and people with a history of substance use disorder, bipolar disorder, psychosis, or severe anxiety require careful evaluation and monitoring.
Comparative safety: Safety concerns are broadly similar across stimulant ADHD medications, with main risks involving cardiovascular effects, appetite and sleep changes, and potential for misuse or dependence; non-stimulant ADHD medicines may be preferred when these risks are unacceptable.
Reporting side effects and safety updates: Side effects can be reported to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) through the MedWatch program (online or by phone) or through a pharmacist or clinician, and safety communications and label updates are available on the FDA’s drug safety web pages.
Interactions and Precautions
Key drug interactions: This medicine must not be used with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days of stopping an MAOI because of the risk of dangerously high blood pressure or serotonin syndrome. Caution is needed when combining with other medicines that increase serotonin (such as many antidepressants, some migraine medicines, and certain pain or cough medicines), as well as with other stimulants. It may reduce the effectiveness of some blood pressure medicines and interact with drugs that change urine pH (such as some antacids or acidifying agents), which can alter stimulant levels in the body.
OTC products, supplements, foods, and alcohol: Decongestants and other stimulant-containing cold or allergy medicines can add to heart and blood pressure effects and are usually avoided or limited. Large amounts of acidic foods or drinks (such as citrus juices or vitamin C supplements taken near the dose) can modestly reduce absorption, while certain antacids can increase blood levels. Alcohol can worsen side effects like impaired judgment and may affect how extended-release products release the drug, so it is best avoided.
Conditions requiring precautions: Extra caution and individualized risk–benefit assessment are needed in people with heart disease, high blood pressure, hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, severe anxiety or agitation, tics or Tourette syndrome, bipolar disorder or psychosis, a history of substance use disorder, or severe kidney disease. Baseline evaluation for cardiovascular risk factors is recommended before starting therapy.
Monitoring needs: Blood pressure and heart rate should be checked at baseline and periodically during treatment; children and adolescents should have their height and weight monitored regularly for growth effects. Clinicians may monitor mood, behavior, and any signs of misuse or diversion, and some patients with heart disease or strong family histories of sudden cardiac death may need additional heart evaluation such as an ECG based on clinical judgment.
Common Questions and Answers
Q: How long does it take for this medicine to start working?
A: Immediate-release tablets often begin to work within 30–60 minutes, and extended-release capsules typically start working within a couple of hours, with noticeable improvement in focus and alertness the same day at an effective dose.
Q: How long do the effects last?
A: Immediate-release doses usually last about 4–6 hours per dose, while extended-release formulations are designed to last most of the school or work day, often around 10–12 hours, though this varies by person and product.
Q: Can I stop taking it on weekends or holidays?
A: Some people use “drug holidays” under a clinician’s guidance to reassess symptoms or help with appetite and growth, but you should not start or stop the medicine, or change the schedule, without first discussing it with your prescriber.
Q: Will this medicine cure ADHD?
A: It does not cure ADHD or narcolepsy, but it can greatly reduce symptoms and improve daily functioning while you are taking it; benefits usually diminish when the medication is stopped.
Q: Is it addictive?
A: This medicine has a risk of misuse, dependence, and diversion because it is a stimulant, especially if taken in higher-than-prescribed doses or by people without a medical need, so it should be used exactly as directed and never shared.
Q: Can children take this medication safely?
A: When prescribed appropriately and monitored regularly, many children use this medicine safely and effectively, but their growth, heart rate, blood pressure, appetite, sleep, and mood should be checked routinely and the lowest effective dose used.
Better Treatment, Lower Cost – No Catch.
Find safer, more effective medications with fewer side effects – often for less money. It’s fast, free, and personalized. Learn More →
Disposal Guidance
Storage: Store at room temperature (generally 68–77°F or 20–25°C), away from excess heat, moisture, and light, and keep the bottle tightly closed and out of reach of children, teens, and pets.
Safe-keeping: Because it is a Schedule II controlled substance with abuse potential, keep it in a secure place, do not share it with others, and track the number of pills remaining.
Disposal: Use a drug take-back program if available, or follow pharmacy or local guidelines for disposing of unused tablets or capsules; do not flush unless specifically instructed, and mix unwanted medication with an undesirable substance (like used coffee grounds or kitty litter) in a sealed container before discarding in household trash if no take-back option exists.