At a Glance

How It Works
- Modafinil acts on several brain chemicals (including dopamine, norepinephrine, and orexin systems) to promote wakefulness and reduce the tendency to fall asleep.
- It modestly increases certain neurotransmitters by blocking dopamine reuptake, which helps you feel more alert without the strong “jolt” of traditional stimulants.
- It has a lower risk of dependence than many classic stimulants but can still be habit‑forming if misused.
Treatment and Efficacy
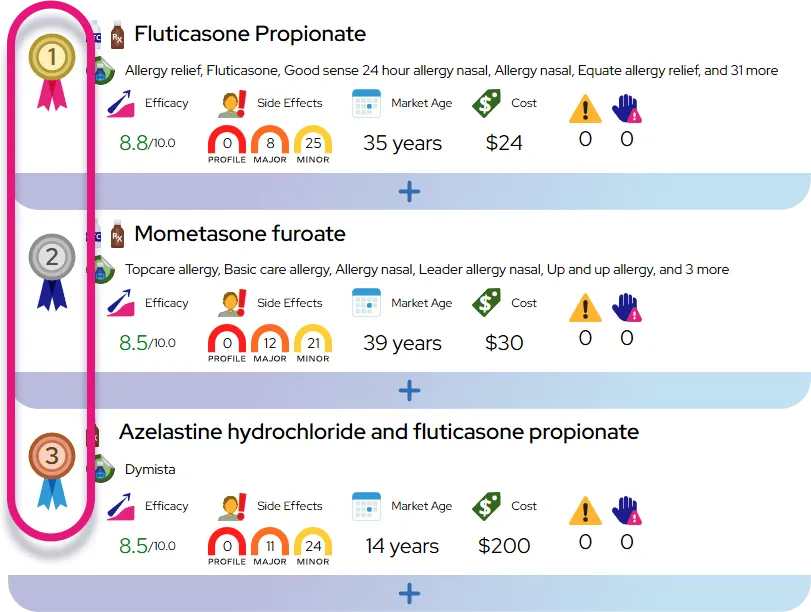
Approved indications: Modafinil is FDA‑approved in adults to promote wakefulness in excessive sleepiness due to narcolepsy, obstructive sleep apnea (as an add‑on to primary airway therapy such as CPAP, not a replacement), and shift work sleep disorder.
Off‑label uses and evidence: Clinicians sometimes prescribe modafinil off‑label for conditions such as fatigue related to multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, depression, cancer or its treatments, and for attention‑deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or cognitive enhancement; evidence ranges from modest benefit in some fatigue syndromes to mixed or limited data in ADHD and cognitive performance, and it is not FDA‑approved for these uses.
Efficacy expectations: Many patients notice increased alertness within the first few days, often after the first dose; in clinical trials, modafinil improves objective sleepiness scales and ability to stay awake, but it does not cure the underlying sleep disorder or fully normalize sleep in all patients.
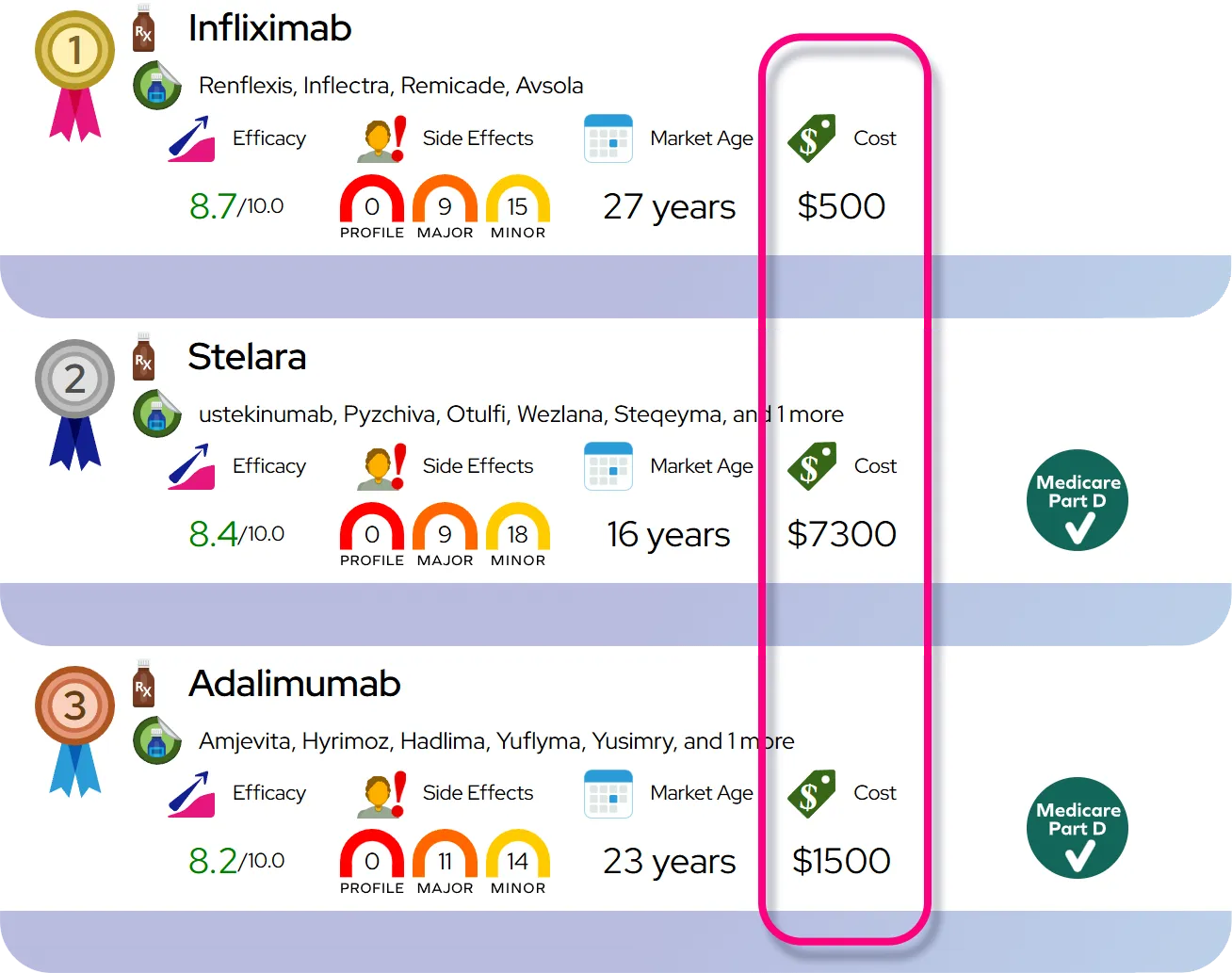
Comparison to similar drugs: Compared with traditional stimulants (such as amphetamines or methylphenidate), modafinil generally causes less jitteriness, appetite loss, and cardiovascular stimulation and has a lower abuse potential, but its wake‑promoting effect can be somewhat milder for some individuals.
Dosage and Administration
Typical dosing and how to take: For adults with narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea, a common starting and maintenance dose is 200 mg by mouth once each morning; some patients may be prescribed up to 400 mg daily, usually as a single morning dose or split into morning and midday doses, depending on response and tolerability.
For shift work sleep disorder, the usual dose is 200 mg taken about 1 hour before the start of the work shift; tablets may be taken with or without food, but a high‑fat meal can delay the onset of effect, so consistent timing with respect to meals is helpful.
Special dosing instructions: Because modafinil can interfere with sleep, it is generally taken early in the day for daytime sleepiness and avoided in the late afternoon or evening unless specifically prescribed for night‑shift work; dose adjustments may be needed in significant liver impairment or in older adults, and it should be taken exactly as directed without increasing the dose on one’s own.
Missed dose guidance: If you miss a morning dose and it is still early, take it when remembered, but if it is close to your usual bedtime or late in the day, skip the missed dose to avoid insomnia; if you miss the pre‑shift dose for shift work, usually you skip that dose rather than taking it late.
Overdose: In case of suspected overdose (such as taking much more than prescribed or combining with other stimulants), call poison control or emergency services right away; symptoms can include severe restlessness, anxiety, trouble sleeping, fast or irregular heartbeat, high blood pressure, nausea, or hallucinations.
Safety and Side Effects
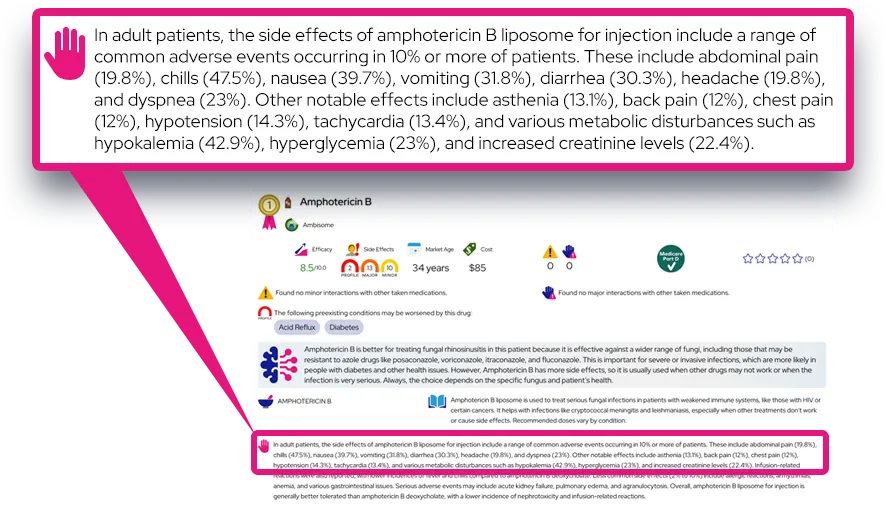
Common side effects: Frequently reported effects include headache, nausea, decreased appetite, anxiety, nervousness, and insomnia; these often appear early in treatment, are usually mild to moderate, and may improve as the body adjusts or with dose or timing changes.
Serious or rare adverse effects: Seek urgent medical attention for rash (especially with blistering, peeling skin, mouth sores, or fever), as modafinil has been associated with rare but severe reactions such as Stevens‑Johnson syndrome and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), as well as for signs of allergic reaction (swelling of face, lips, tongue, trouble breathing), chest pain, irregular heartbeat, hallucinations, extreme agitation, suicidal thoughts, or severe mood changes.
Warnings and precautions: Modafinil is not routinely recommended in children due to higher risk of serious rash; use cautiously or avoid in people with a history of left‑ventricular hypertrophy, mitral valve prolapse with stimulant‑induced issues, significant heart disease, or uncontrolled high blood pressure, and discuss any history of mental health disorders (such as psychosis, mania, or severe anxiety) or substance use disorder with the prescriber.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Data in pregnancy are limited and some reports suggest possible increased risk of birth defects; effective contraception is essential and hormonal birth control (pills, patch, ring, implants, some IUDs) can be less effective while taking modafinil and for about a month after stopping, so backup or alternative non‑hormonal methods are advised; breastfeeding safety is uncertain, so the risks and benefits should be carefully discussed.
Overall safety profile: Compared with many traditional stimulants, modafinil often has a somewhat more favorable profile for blood pressure, heart rate, and abuse potential, but it still carries risks of cardiovascular, psychiatric, and serious dermatologic reactions, and it is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance in the U.S.
Reporting side effects and safety updates: Patients and caregivers can report suspected side effects to the FDA MedWatch program (online or by phone) and should periodically review medication guides or talk with their healthcare team for the latest safety information.
Interactions and Precautions
Drug and supplement interactions: Modafinil can reduce the effectiveness of many hormonal contraceptives and may lower blood levels or effects of some medicines (for example certain birth control pills, cyclosporine) while increasing levels of others (such as some benzodiazepines, certain antidepressants, and antiepileptic drugs) through its effects on liver enzymes; interactions are also possible with other stimulants, decongestants, caffeine, and herbal products like St. John’s wort.
Food, alcohol, and other substances: Food does not greatly change the overall amount absorbed but a high‑fat meal can delay onset; alcohol’s effects may be less predictable when combined with modafinil, so limiting or avoiding alcohol is generally advised.
Conditions requiring extra caution: Use with caution or avoid in patients with significant heart disease, uncontrolled hypertension, structural heart abnormalities, serious arrhythmias, a history of mania, psychosis, or severe anxiety, or a history of substance use disorder; close supervision is recommended when combining with other medications that affect the heart, blood pressure, or mental state.
Monitoring needs: Healthcare providers may periodically check blood pressure, heart rate, and mental status, and review all medications for interactions; in people with liver disease or on multiple interacting drugs, additional lab monitoring and dose adjustments may be needed.
Common Questions and Answers
Q: How long does it take for modafinil to start working and how long does it last?
A: Many people feel more awake within 1–2 hours of taking a dose, with wake‑promoting effects often lasting most of the workday or shift (about 8–12 hours), although this can vary between individuals.
Q: Is modafinil the same as a traditional stimulant like Adderall?
A: No, modafinil is a wake‑promoting agent with a different mechanism and generally milder effects on heart rate, blood pressure, appetite, and mood, though it can still have stimulant‑like properties and a risk of misuse.
Q: Can I drink coffee while taking modafinil?
A: Many people do, but combining modafinil with large amounts of caffeine can increase side effects such as jitteriness, anxiety, palpitations, or trouble sleeping, so it is best to limit total stimulant intake and adjust based on how you feel.
Q: Will modafinil interfere with my birth control?
A: Yes, modafinil can make many hormonal contraceptives (pills, patch, ring, implant, some IUDs) less effective, so using a reliable non‑hormonal or backup method during treatment and for about one month after stopping is recommended.
Q: Is modafinil safe to take every day for a long time?
A: Some people use modafinil long term under medical supervision, but ongoing follow‑up is important to monitor blood pressure, heart and mental health, sleep patterns, and the continued need for the medication, as well as to reassess the underlying sleep disorder.
Better Treatment, Lower Cost – No Catch.
Find safer, more effective medications with fewer side effects – often for less money. It’s fast, free, and personalized. Learn More →
Disposal Guidance
Storage: Keep modafinil tablets at room temperature (about 68–77°F or 20–25°C), in a tightly closed container, away from moisture, heat, and direct light, and out of reach of children and pets.
Disposal: Use a drug take‑back program if available, or follow local guidance for mixing unused tablets with an undesirable substance (like coffee grounds or cat litter) in a sealed container before throwing in the household trash; do not flush unless specifically instructed.