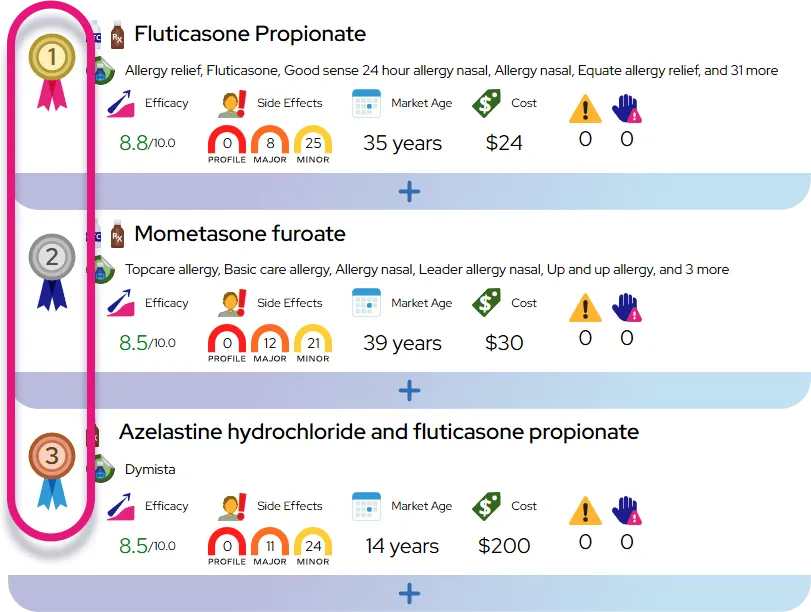
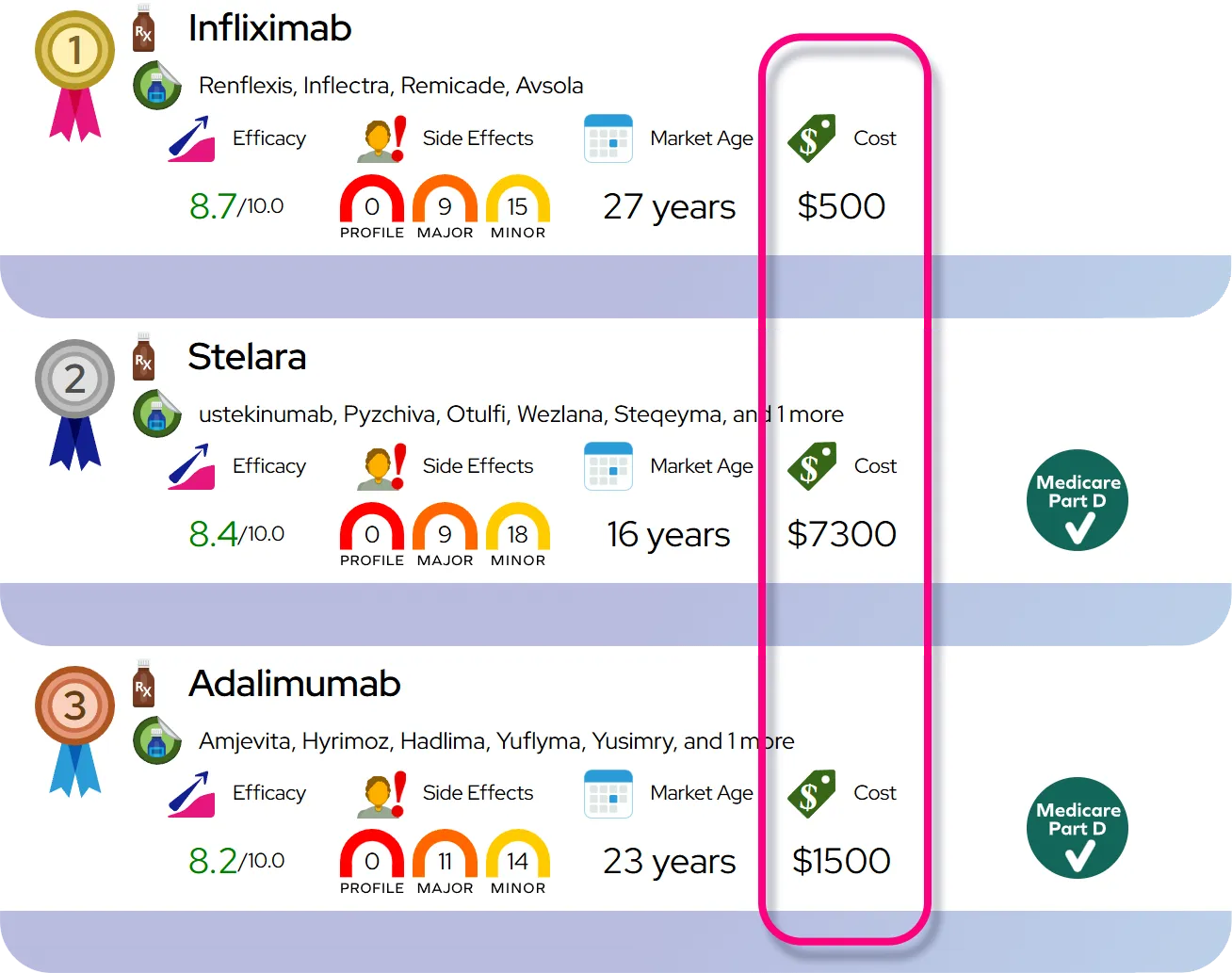
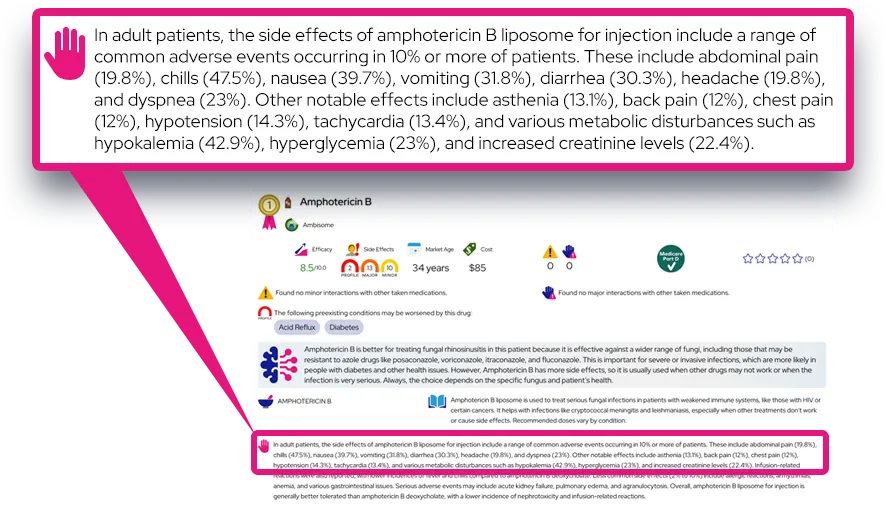
At a Glance
How It Works
- Transdermal methylphenidate is a stimulant that helps increase levels of natural brain chemicals called dopamine and norepinephrine.
- These chemicals improve communication between brain cells in areas that control attention, impulse control, and activity level.
- By improving these signals, it can help people with ADHD focus better, sit still longer, and reduce impulsive behaviors.
Treatment and Efficacy
Approved indications
- Transdermal methylphenidate is approved to treat ADHD in children and adolescents ages 6–17 years who need once-daily stimulant treatment and may benefit from a patch instead of pills.
Off-label uses and evidence
- Clinicians may sometimes use transdermal methylphenidate off-label in adults with ADHD when an oral methylphenidate product is not suitable, but evidence is more limited than for standard oral formulations.
- Other possible off-label uses (such as narcolepsy) are usually treated with oral stimulants instead, so transdermal use for these conditions is uncommon and less studied.
Efficacy expectations
- Effects usually begin within about 2 hours after the patch is applied, with symptom improvement during the school or work day while the patch is worn.
- Many patients show better attention, less hyperactivity, and improved school or social functioning, though some may need dose adjustments or different stimulants to get optimal benefit.
- Compared with oral methylphenidate, overall ADHD symptom control is generally similar when equivalent doses are used, but the patch can offer more flexible duration (by removing it earlier) and may help patients who cannot swallow pills or need supervised dosing.
Dosage and Administration
Typical dosing and how to use
- For children and adolescents 6–17 years, treatment often starts with a 10 mg/9-hour patch applied once daily to a clean, dry, hairless area on the hip, usually in the morning; the dose may be increased in steps (e.g., 15, 20, up to 30 mg/9 hours) based on response and tolerability.
- Apply the patch to the same hip area for a day and rotate hip sites daily to reduce skin irritation; press firmly so all edges stick well.
- The patch is usually worn for up to 9 hours, then removed; symptom duration can be shortened by taking it off earlier in the day as instructed by the prescriber.
- Do not cut the patch, and avoid exposing it to direct heat sources (heating pads, electric blankets, very hot baths) that could increase drug absorption.
Special dosing instructions
- If significant skin irritation occurs, the prescriber may change the application schedule, recommend topical treatments, or switch medications.
- Doses should be adjusted only by the prescriber; caregivers should not change patch strength or wear time on their own.
Missed dose guidance
- If you forget to apply the patch at the usual time but remember later in the morning, apply it when remembered while still allowing enough time to remove it at the usual hour so that sleep is not affected.
- If it is late in the day, skip the missed dose and apply a new patch the next morning; do not apply extra patches to make up for a missed dose.
Overdose
- In case of overdose or if multiple patches were applied, remove all patches immediately and seek emergency medical help or call a poison control center, especially if there are symptoms like severe agitation, vomiting, chest pain, rapid heartbeat, tremors, or confusion.
Safety and Side Effects
Common side effects
- Common effects include decreased appetite, weight loss, trouble sleeping, stomachache, headache, irritability, and nausea; skin redness or itching under the patch is also frequent.
- These usually appear soon after starting treatment or changing the dose and are often mild to moderate; some improve over time or with dose or schedule adjustments.
Serious or rare adverse effects
- Seek immediate medical attention for chest pain, shortness of breath, fainting, a fast or irregular heartbeat, severe aggression or mood changes, hallucinations, or signs of allergic reaction (swelling of face/lips, trouble breathing, widespread rash).
- Rare but serious problems can include sudden cardiac events in people with underlying heart disease, severe high blood pressure, new or worsening psychosis or mania, seizures, or prolonged, painful erections (priapism).
- Persistent, severe skin reactions at the application site, blistering, or signs of systemic allergic reaction to the patch also require urgent evaluation.
Warnings and precautions
- Not recommended for people with known serious structural heart problems, certain heart rhythm disorders, or moderate-to-severe high blood pressure unless a specialist determines it is safe.
- Use with caution in people with a history of substance misuse, tics or Tourette’s disorder, seizures, bipolar disorder, or serious anxiety, as symptoms can worsen.
- In pregnancy, stimulants are used only if the potential benefit justifies possible risks; breastfeeding decisions are individualized because small amounts of drug may pass into breast milk.
- Older adults rarely use this transdermal form; careful monitoring is needed if prescribed, especially for cardiovascular issues.
Relative safety compared with other drugs
- Safety concerns are broadly similar to other stimulant ADHD medications (e.g., oral methylphenidate or amphetamines), with added attention to skin reactions at the patch site.
- Nonstimulant ADHD medications may be preferred for patients who cannot tolerate stimulant side effects or have particular cardiac or psychiatric risks.
Side effect reporting and safety updates
- Patients and caregivers can report side effects to the prescriber and to the FDA MedWatch program and should periodically review updated medication guides or FDA safety communications for new warnings regarding stimulant medications.
Interactions and Precautions
Drug and supplement interactions
- Do not use transdermal methylphenidate with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days of stopping an MAOI due to the risk of dangerous blood pressure elevations.
- Other medicines that can raise blood pressure or heart rate (some decongestants, asthma drugs, certain antidepressants) may increase cardiovascular side effects when combined.
- Some antidepressants, antipsychotics, and seizure medications may interact with stimulants and require dose adjustments or monitoring.
- Caution is advised with herbal products that affect mood or blood pressure (such as St. John’s wort or high-dose caffeine products).
Food, alcohol, and other interactions
- Food does not significantly affect absorption from the patch, but heavy evening meals or caffeine close to bedtime can still worsen insomnia for some patients.
- Alcohol can increase heart rate and impair judgment; combining alcohol with stimulants may mask intoxication and is generally discouraged.
Conditions requiring extra precautions
- Use with particular care or avoid in people with known heart disease, structural cardiac abnormalities, serious arrhythmias, moderate-to-severe hypertension, hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, or a history of drug misuse.
- Additional caution and close monitoring are needed in patients with bipolar disorder, psychosis, seizures, or severe anxiety, as symptoms may be aggravated.
Monitoring needs
- Blood pressure, heart rate, weight, and height (in children) are typically checked regularly during treatment.
- A detailed cardiovascular history and exam are recommended before starting; an ECG may be obtained when there is a personal or family history of heart problems or other concerning findings.
- Periodic review of ADHD symptoms, sleep, appetite, mood, and skin reactions at the patch site helps guide dose and treatment adjustments.
Common Questions and Answers
Q: How long does the methylphenidate patch last during the day?
A: The patch is usually worn for up to 9 hours, with effects often continuing a few hours after removal; your prescriber may adjust wear time to cover school or work hours while minimizing sleep problems.
Q: Can my child shower, swim, or play sports while wearing the patch?
A: Normal activities, including bathing and sports, are usually allowed, but very hot water, saunas, or direct heat sources should be avoided, and if the patch falls off, follow the product instructions or call your prescriber about whether to apply a new one.
Q: What if my child has skin irritation where the patch was?
A: Mild redness that fades after removal is common, but if there is persistent pain, swelling, blistering, or a widespread rash, contact the prescriber; rotating application sites and ensuring the skin is clean and dry before application can help reduce irritation.
Q: Will my child need to take the patch every day, including weekends?
A: Some children use the patch only on school days, while others benefit from daily use; decisions about “drug holidays” should be made with the prescriber based on symptom control, side effects, and growth monitoring.
Q: How is the patch different from oral ADHD medicines?
A: The medication inside is similar to oral methylphenidate, but the patch delivers it steadily through the skin, can be removed to shorten duration if needed, and may be easier for children who cannot swallow pills or need supervised dosing.
Better Treatment, Lower Cost – No Catch.
Find safer, more effective medications with fewer side effects – often for less money. It’s fast, free, and personalized. Learn More →
Disposal Guidance
Storage
- Store patches at room temperature, tightly sealed in the original pouch until use, away from heat, moisture, and direct sunlight.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets, and do not store in the bathroom where humidity is high.
Disposal
- After removing, immediately fold the used patch in half with the sticky sides together so the medication is not exposed.
- Place folded patches in a secure container or dispose of them in household trash where children and pets cannot reach them; do not flush patches down the toilet unless the product instructions specifically allow this.
- If local drug take-back programs are available, use them for unused or expired patches.